Most computers have software that records or logs the user’s information. For the most part, it’s so that the user can access and use it themselves in a secure manner. However, methods can disrupt security and let third parties access the user’s information.
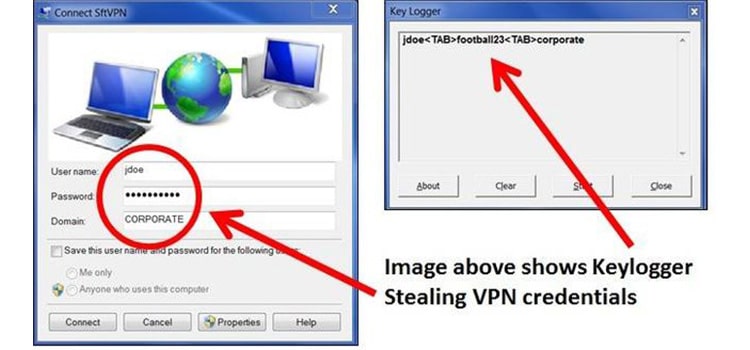
Keystroke logging records every keystroke on the keyboard and can give a record of potentially sensitive information to a third party online through software or specialized hardware through a keylogger. Keyloggers may be hard to detect, but several measures against them and remove them.
Despite how intimidating they can sound, the following article can break down the general concept to let most laymen have a basic understanding of keystroke logging and keyloggers and some security measures to make.
What is Keystroke Logging?
Keystroke logging is defined as the record-keeping of every stroke made on a keyboard. Keystrokes are any press of a button on a keyboard, and so is one of the primary ways you can input and output information to your computer. Keystroke logging gives third-party users access to whatever information one put out or typed in without the user knowing.
Keystroke logging can detect which button was pressed, how long the user pressed it, and how fast they were done. Should a compilation be made from this data, keystroke logging can pool together extremely personal details and sensitive information from a keyboard. You can also do this with or without the computer user’s consent.
What are Keyloggers?

Keystroke logging is the general concept of recording the input, and keylogging is the software, or hardware, used to do just that. Keylogging works by recording all the input sent and putting them into an accessible file for later use. Keyloggers can also vary in terms of scope, and others can range from the copy-paste clipboard from the usual buttons to microphone and camera footage and audio.
That said, keyloggers are not inherently illegal by themselves. Keyloggers are often used within the IT field for ease of feedback and support purposes. It can also be used for monitoring, like monitoring devices in public areas, in order to ensure general safety and legal usage.
How Keystroke Logging Works
As previously mentioned, keystroke logging and keyloggers are legal and see a fair amount of usage in modern times. These uses range from small-scale, personal objectives like a parent-child monitoring system to large-scale operations like software monitoring from and for IT departments of companies. These justifications are fairly subjective, though, and the legality of keystroke logging and keyloggers does not subtract from the harm they can cause when used with malicious intent.
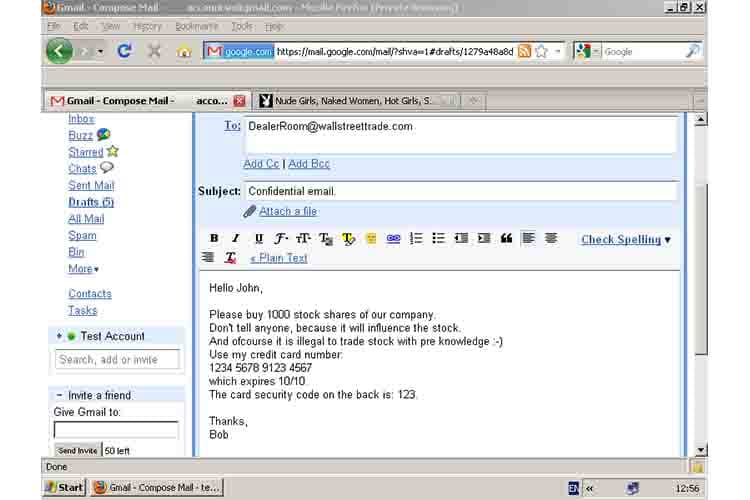
When in the hands of those who want to use them for non-consensual information gathering, keystroke logging and keyloggers can still extract sensitive data from an unknowing user. This information can range from passwords all the way to bank names and codes. Phishing emails often come with keylogging to gain third-party access to the computer to which the email was sent.
Keystroke logging can even be included in various programs downloaded, hidden within a lengthy Terms of Service to make it hard to find, or when a user chooses to do an automatic install without checking. In these instances, keystroke logging is technically legal since they were able to get the consent of the user.
Types of Keyloggers
Software-Based Keyloggers
A keylogging software program allows remote access to a third party to a computer unit without physical access to itUsers can download it on purpose for the express use of monitoring certain activities or programs on a select computer or to monitor a user’s device with the user’s consent. It can also be downloaded unwittingly as part of another software, either as a buried part of the Terms of Service, or a part of a rootkit, so it can operate without interference from antivirus scans or even manual detection.
Commonly, keylogging software consists of a DLL file to record the information and an executable that installs the DLL to trigger it. The software then records any and all keystrokes the user makes and sends the information over the internet at scheduled times. It can also be used to remotely install malicious scripts and other various malware.
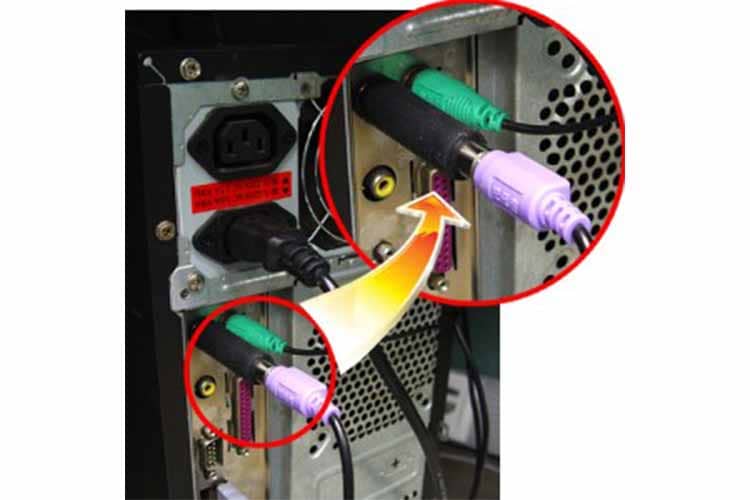
Hardware-Based Keyloggers
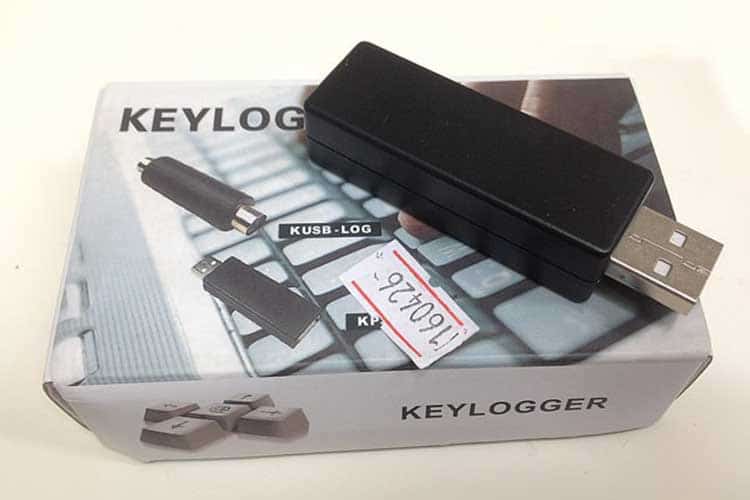

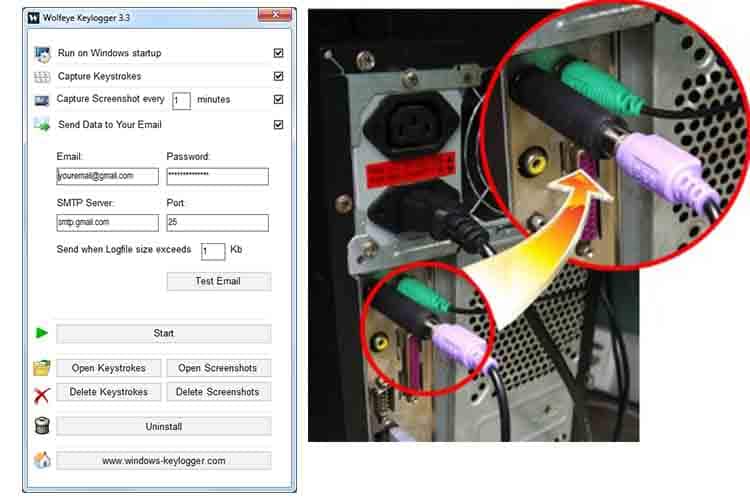
Unlike the keylogging software, the keylogging hardware requires physical access to the chosen computer target. The hardware itself is designed to be innocuous, to look like a common computer accessory or cable, like a USB or a wireless connector for peripherals. This is in order for it to be easily hidden for continued usage and is often plugged into the back of the CPU tower. Another type of hardware keylogger can even be installed within a keyboard.
When users interact with their keyboard, the keylogger records all the data made and stores it within the attached hard drive. This data is limited to the memory capacity it comes with. Unlike the software keylogger, the hardware keylogger has to be physically removed by the third-party user at a later time.
Where are Keyloggers Used?
Keyloggers are not exactly modern inventions; they’ve been in use for decades, as far back as the 1970s, within covert operations by governments during periods of strife or for data gathering. Currently, though, keyloggers are in the top ten of the most common malware in usage, often within industrial and enterprise fields. There are two types of keyloggers; the legal ones and the illegal ones.
Legal keylogging can be used for various situations, mostly in the technical field for repair and monitoring. For the most part, it depends on the user’s intentions. Examples of legal keylogging are monitoring devices in public institutions like libraries, computer troubleshooting, and repair, or any legal usage consented by the user.
Illegal keylogging has been mentioned before; usage of keylogging with the goal of gaining sensitive information, among other things. Illegal keylogging can also account for theft, stalking, voyeurism, or something as simple as installing the software/hardware when there was a legal clause to promise otherwise.
Are Keyloggers a Virus?
A virus is defined as anything coded to alter a computer’s operation, and while keyloggers can often have suspect uses, they are not illegal to install and use. Keyloggers are mostly regarded as malware instead. Malware, short for malicious software, is often how keyloggers are used within illegal contexts.
A virus, though, is a code that is attached to a file that can lock a user out of files, encrypt the information or steal data. It is entirely illegal. Since keyloggers are classified under malware, the type of malware they are called is spyware. These are software that operates under malicious intent but without detection, needing the target to operate while under the assumption that all is well.
How to Detect Keyloggers?
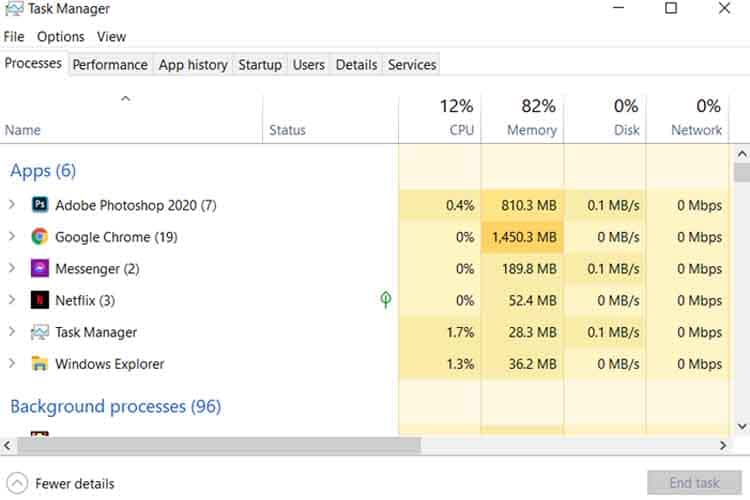
The simplest way a person can detect any malware on their computer is to look at the Task Manager. The Task Manager lists through all the open and running programs on the computer at any given time. Modern task managers even give out statistics about hardware components.
When you look into the Task Manager, you can search and look for any software or program that does not belong. It’s also prudent to remove anything you don’t remember installing among your files. And one last thing is to look through your internet usage and see through to comb for suspicious activity or extensions you didn’t install yourself.
Ways to Prevent Keystroke Logging
Seeing as keyloggers are meant to be covert, detecting them is fairly complicated. There are some steps and precautions to observe safety against them, such as:
Attachments can carry malware from even legitimate software. Any file received can carry such, and Antivirus can generally detect them.
Updating everything on the computer is also a great defense against most malware. Most software and computer systems have built-in defenses against most malware and viruses. Being late on updates renders a computer vulnerableCurrently, there are even cyber security offers online that can do most of the technical lifting for you.
Protection Tools and Methods
If a user wants to protect themselves against keyloggers as part of their general cybersecurity stratagem, the following tools and methods may help, depending on the level needed:
Application Whitelisting
Whitelisting is a lockdown measure. It is where a user can only interact with select programs an administrator had given them access to. It makes it severely less functional than a regular computer unit and requires ongoing specialized maintenance.
For the above reason, it’s considered an extreme solution to cybersecurity problems, and it’s generally not the first recommendation when needing a general defense against keyloggers and other malware.
Antikeylogging Software
Much like the name suggests, an anti-keylogger can identify and root out a keylogger even when it is well-hidden. It’s designed to detect and identify and allows users to remove the keylogger entirely, and this can prevent any sensitive or critical data from being stolen.
An anti-keylogger can monitor a computer’s behavioral patterns to pick out any oddities within the system, scan various applications in case a keylogger was an added attachment, and separate any suspicious software into a sandbox.
Network Monitors
Monitoring tools are made to record and track critical applications and software on systems. They can also track large-scale infrastructures, networks, and websites. They alert administrators for any problems within the systems to dispatch any repairs in due time. This means that users can detect keyloggers, and they can resolve the problem.



